Understanding NeRFs: The Future of Imaging Technology
Written on
The Rise of a New Imaging Medium
Throughout history, we have witnessed the emergence of groundbreaking mediums that not only push technological boundaries but also capture the public's imagination. Photography, for instance, has undergone numerous fascinating advancements over time.
Instant film cameras, like Polaroids, became a hit for their ability to produce immediate prints without the hassle of film development. The advent of digital photography further transformed the landscape by simplifying the process and granting photographers enhanced control over their images. Platforms such as Instagram made sharing photos effortless, fostering a vibrant community around photography and integrating it with social media.
Today, we stand on the brink of a transformative new imaging technology known as Neural Radiance Fields, or NeRFs.
What Exactly is a NeRF?
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) represent a sophisticated class of neural networks that can generate new viewpoints of complex 3D environments using a limited number of 2D images. By leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms, NeRFs can convert 2D visuals into 3D representations, offering a more intricate depiction of objects or entire scenes.
The process is quite remarkable...

In essence, when presented with a series of images of an object captured from various angles, the neural network learns to construct a 3D model that can generate novel views of the subject.
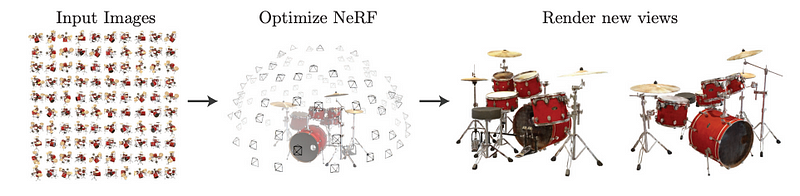
You might be thinking, isn't it tedious to take multiple images that have to be stitched together? The good news is that mobile applications like Luma AI now make it incredibly simple to produce NeRFs right from your smartphone. For developers, tools like Nvidia's NGP Instant NeRF, TurboNeRF, and NeRFStudio offer robust resources for experimentation, while Luma's user-friendly interface opens the technology to a broader audience. As more applications like Luma emerge, we can anticipate a significant increase in NeRF adoption, marking a new phase in digital photography.
Why is This Important?
While traditional 2D photographs have their unique appeal, interactive 3D images elevate the experience to a new dimension. They are not only more captivating but also provide a richer and more immersive engagement.
Imagine a scene like this...
Shaha skate spot Varna, Bulgaria - Created by @luxdigital with Luma
Capture the world in lifelike 3D
lumalabs.ai
The “camera of the future” might look similar, but the way content is manipulated and experienced will be transformed. Viewers are no longer restricted to the perspective captured by the original photographer; they can explore a NeRF infinitely, discovering the angle and viewpoint that resonates most with them.
- Michael Rubloff
NeRFs: A Game-Changing Medium
NeRFs are particularly compelling due to their wide-ranging applications across various sectors, including architecture, real estate, video games, film VFX, and scientific visualization. They can generate intricate and realistic 3D environments for virtual and augmented reality experiences, from virtual tours to educational simulations that allow users to explore historical sites or scientific concepts in three dimensions.
In the film and video industries, NeRFs can create lifelike 3D models of sets or locations and can be employed for special effects or previsualization during production. Furthermore, they have the potential to craft avatars and scenes for virtual environments, capture participants in 3D during video conferences, and reconstruct scenes for 3D digital maps.
Check out Luma’s NeRF plugin for Unreal Engine 5:
NeRFs are also emerging as novel forms of artistic expression. For instance, the music video "Pour Your Heart Out" by RL Grime showcases the capabilities of NeRF technology.
Are NeRFs Just Another Form of Photogrammetry?
A discerning digital artist might question the uniqueness of NeRFs, given that photogrammetry has been a technique for 3D reconstruction from photographs for many years. While both NeRFs and photogrammetry serve similar purposes, NeRFs offer significant advancements that enhance their capabilities.
NeRFs can adeptly manage complex lighting conditions, inferring lighting information from the input images and applying it to the reconstructed scene. As a form of generative AI, NeRFs can render images from any angle, even those not captured in the original images, allowing for more authentic and immersive 3D experiences.
Conclusion
As our world shifts toward spatial computing and 3D imagery becomes increasingly prominent, NeRFs are poised to elevate imaging technology to unprecedented heights. The potential uses for NeRFs are extensive, and we can expect to see this innovative technology integrated into an expanding array of industries in the near future.
If you found this article insightful, don't hesitate to show some love on Medium—claps, comments, and follow! You can also support my work on Medium by becoming a member using this referral link.
The Next Wave of NeRF Insights
The first video, "Why do we need nerfs in PVE?" explores the necessity of nerfs in player versus environment scenarios, shedding light on balance and gameplay dynamics.
The second video, "ALL NERFS AND BUFFS REVEALED! Are the NERFS enough? How BROKEN are the BUFFS? Is Wild saved?" dives into the details of nerfs and buffs in gaming, questioning their effectiveness and impact on the gaming landscape.